
Performing full WordPress backups protects your site from catastrophic data loss from server crashes, hacks, or accidental data deletions. Without regular backups, you could permanently lose all your WordPress site content, users, settings, and plugins if any potential data loss factors occur.
Manually backing up your WordPress site is time-consuming and involves constant execution steps. If you rely on manual backups, you may skip an important backup, hence, automating the backup process ensures that your backup files are always up to date. This article explains how you can automate the full WordPress backup process using the following Linux tools:
By combining the tool functionalities, you will create an automated backup script to regularly perform a full WordPress backup. Then, you will upload the full backup to Dekopon Stack Object Storage for restoration at a specific point in time.
Before you begin:
wp-files as the Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket name. webadmin for the non-root user with sudo access and example.com for the WordPress domain. Replace these values with your actual WordPress server details.Rclone is a command-line utility used to manage files stored on cloud storage volumes. It performs file synchronization tasks similar to other common utilities such as RSync. Follow the steps below to install Rclone and use it to manage files on your Dekopon Stack Object Storage Bucket.
Download and install the latest Rclone installation script.
$ curl https://rclone.org/install.sh | sudo bash
Output:
rclone v1.64.2 has successfully installed.
Now run "rclone config" for setup. Check https://rclone.org/docs/ for more details.Test the Rclone configuration to verify that it's installed correctly.
$ rclone config file
Output:
Configuration file doesn't exist, but rclone will use this path:
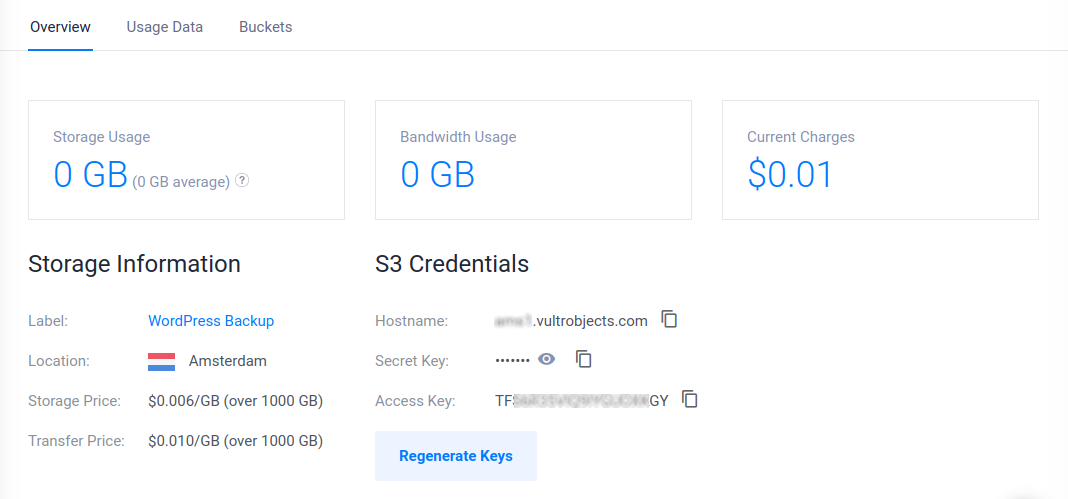
/home/webadmin/.config/rclone/rclone.confTo configure rclone to use your Dekopon Stack Object Storage details, access the Dekopon Stack Customer Portal. Then, copy your Dekopon Stack Object Storage authentication details including the Hostname, Access Key, and Secret Key from the Overview tab
Open the Rclone config file using a text editor such as Nano.
$ nano /home/webadmin/.config/rclone/rclone.conf
Add the following configurations to the file to create a new remote location wp-backup that points to your Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket.
[wp-backup]
type = s3
provider = Other
env_auth = false
access_key_id = YOUR_ACCESS_KEY
secret_access_key = YOUR_SECRET_KEY
region =
endpoint = https://endpoint
location_constraint =
acl = private
server_side_encryption =
storage_class =
Save and close the file.
The above configuration creates a new Rclone remote storage profile wp-backup that points to your Dekopon Stack Object Storage. Replace the placeholder values, and https://endpoint with your actual hostname such as https://ams1.Dekopon Stack objects.com to correctly enable your Dekopon Stack Object Storage connection. This allows you to use Rclone commands such as rclone copy to copy files to your storage bucket.
View the list of Rclone remote profiles and verify the new wp-backup profile.
$ rclone listremotes
Output:
wp-backup:Create a sample text file to test your rclone configuration.
$ echo 'This is a test' > testfile.txt
Copy the sample file to your Dekopon Stack Object Storage using Rclone.
$ rclone copy testfile.txt wp-backup:wp-files/
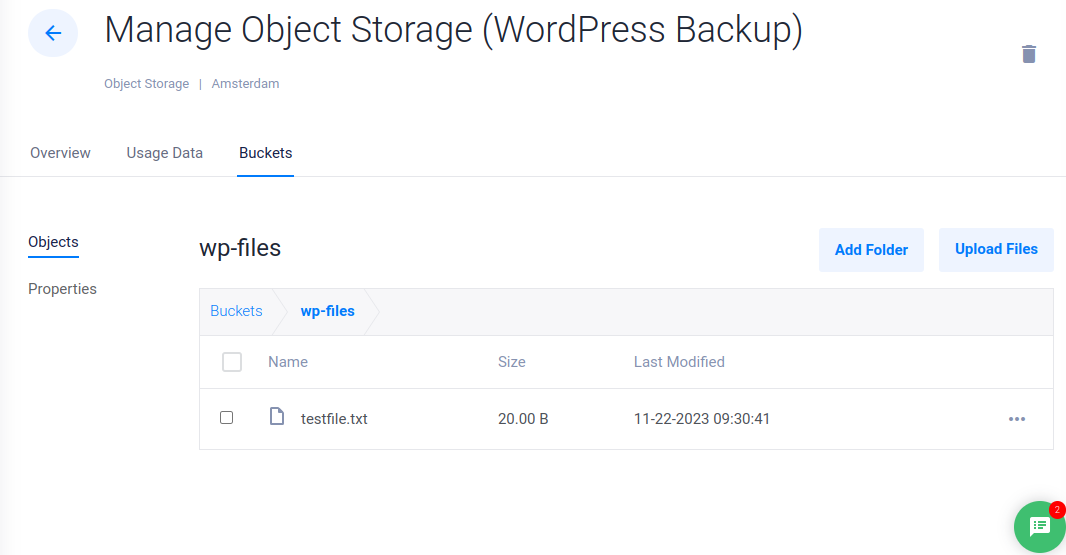
List all files in your wp-files Dekopon Stack Object Storage to verify that the new file is uploaded, and available in your storage bucket.
$ rclone ls wp-backup:wp-files/
Output:
20 testfile.txtAdditionally, access your Dekopon Stack Object Storage file manager and verify that the new sample file is available in your wp-files bucket.
To back up your WordPress site, copy the WordPress database and site files. The database contains all site content, settings, users, and other data while the WordPress files directory contains uploaded files, plugins, themes, and the WordPress core. If you back up the active database and web root directory, you can restore or migrate your WordPress site at any point in time.
To find your WordPress web files directory, view your server host configuration files to identify your working web root directory. For example, when using Nginx, view the host configurations files in the /etc/nginx/sites-available or /etc/nginx/conf.d directories.
Switch to your web server host configuration files directory.
$ cd /etc/nginx/sites-available/
Search all available files for your WordPress domain string using the Grep utility to verify your active host configuration file.
$ grep -r "example.com" .
Output:
/etc/nginx/sites-available/wordpress_https.conf: server_name example.com;Depending on your active configuration file, view the file contents.
$ cat wordpress_https.conf
Within the configuration, find the root directory directive:
root /var/www/example.com;As returned in your output, your WordPress site uses the /var/www/example.com web root directory.
Switch to your WordPress web root directory.
$ cd /var/www/example.com
Long list files in the directory and verify that all WordPress files are available.
$ ls -l
Your output should look like the one below:
total 200
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 405 Feb 6 2020 index.php
lrwxrwxrwx 1 www-data www-data 21 Nov 19 06:56 mysqladmin -> /usr/share/phpmyadmin
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 7211 May 12 2023 wp-activate.php
drwxr-xr-x 9 www-data www-data 4096 Nov 9 00:45 wp-admin
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 351 Feb 6 2020 wp-blog-header.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 2323 Jun 14 14:11 wp-comments-post.php
-rw-rw-r-- 1 www-data www-data 3516 Nov 19 06:57 wp-config.php
drwxr-xr-x 7 www-data www-data 4096 Nov 19 06:58 wp-content
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 5638 May 30 18:48 wp-cron.php
drwxr-xr-x 27 www-data www-data 12288 Nov 9 00:45 wp-includes
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 2502 Nov 26 2022 wp-links-opml.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3927 Jul 16 12:16 wp-load.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 50924 Sep 29 22:01 wp-login.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 8525 Sep 16 06:50 wp-mail.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 26409 Oct 10 14:05 wp-settings.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 34385 Jun 19 18:27 wp-signup.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 4885 Jun 22 14:36 wp-trackback.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 www-data www-data 3154 Sep 30 07:39 xmlrpc.phpCreate a new environment variable WP_ROOT to store the WordPress web root directory path, and append the variable to your ~/.bashrc file.
$ echo 'export WP_ROOT="/var/www/example.com"' >> ~/.bashrc
To record the daily backup time, create a new environment variable BACKUP_TIME with a year, minute, day, and minutes value to record the time each backup starts.
$ echo 'export BACKUP_TIME=$(date +%Y-%m-%d_at_%H.%M.%S)' >> ~/.bashrc
Create a new local backup files directory to store your WordPress backups.
$ mkdir -p /home/webadmin/backups/
Create a new environmental variable to store your backup files directory path.
$ echo 'export BACKUP_DIR="/home/webadmin/backups"' >> ~/.bashrc
Activate your server profile changes to apply the new variables in your session.
$ source ~/.bashrc
Verify that the WordPress web root variable is active and available to use.
$ echo $WP_ROOT
Output:
/var/www/example.comVerify that the backup time variable is available.
$ echo $BACKUP_TIME
Output:
2023-11-19_at_09.57.57The above output verifies that a backup started on 19 November 2023 09:57:57.
Export the WordPress database using WP-CLI to your web root directory.
$ sudo -E wp db export --path=$WP_ROOT $WP_ROOT/db_$BACKUP_TIME.sql --add-drop-table --allow-root
The above command uses WP-CLI to export the WordPress database with the --add-drop-table flag that creates an SQL file with commands to delete existing tables with the same name before recreating them. This helps avoid conflicts and ensures a clean import, especially when overwriting an existing database or restoring a database to a previous state.
Output:
Success: Exported to '/var/www/example.com/db_2023-11-19_at_09.57.57.sql'.Create a compressed WordPress files archive that contains all site files and the .sql file you exported earlier.
$ sudo -E tar -jcvf $BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2 -C $WP_ROOT/.. $(basename $WP_ROOT) --ignore-failed-read
The above command creates a new Tar archive compressed using Bzip2 j that includes all files in the WordPress web root directory to your backup files directory. The --ingore-failed-read flag allows the backup process to continue in case the Tar utility encounters locked files or cannot read some files during the backup process.
List files in your backup files directory and verify that a new .tar.bz2 archive is available.
$ ls -l $BACKUP_DIR
Output:
wp_2023-11-19_at_09.57.57.tar.bz2You have created a full WordPress backup archive that includes all the site files and database. You can transfer the single compressed file to your Dekopon Stack Object Storage and decompress the files when recovering your WordPress site.
Copy the WordPress backup archive from your local backup files directory to your target Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket wp-files using the rclone copy command.
$ rclone copy $BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2 wp-backup:wp-files/
When successful, list the files in your Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket and verify that your WordPress backup file is available.
$ rclone ls wp-backup:wp-files
Output:
15 testfile.txt
28234126 wp_2023-11-19_at_09.57.57.tar.bz2To clear the server storage space, delete the local copy of the WordPress archive
$ rm -rf $BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2
Delete old backup files to avoid running out of space for new backups
$ rclone delete wp-backup:wp-files --min-age 7d
This rclone command deletes all backup files older than 7 days from your Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket. The --min-age option allows you to specify the maximum age of files to keep. You can increase or increase this value. Consult the rclone documentation to see valid time values for this option.
With each backup operation, your Dekopon Stack Object Storage accrues more backup files. The delete command allows you to create space for more recent backups by deleting old ones.
Your WordPress site is now safely backed up in your Dekopon Stack Object Storage bucket. The next step is to automate the backup process.
To automate the WordPress backup process, set up a new Cron task that runs a backup operations script that includes all file transfer commands as described in the steps below.
Using a text editor such as Nano, create a bash script in your user home directory.
$ nano /home/webadmin/wp-backups.sh
Add the following contents to the file.
#!/bin/bash
# Set variables
BACKUP_TIME=$(date +%Y-%m-%d_at_%H.%M.%S)
WP_ROOT="/var/www/example.com"
BACKUP_DIR="$HOME/backups"
RCLONE_CONFIG_FILE="/home/webadmin/.config/rclone/rclone.conf"
LOG_FILE="/var/log/wp_backup_$BACKUP_TIME.log"
MAX_BACKUP_AGE="7d" # Define maximum age of backup files to retain
# Print backup timestamp
echo "Backup time: $BACKUP_TIME"
{
# Create backup directory
mkdir -p "$BACKUP_DIR"
# Export WordPress database
wp db export --add-drop-table --path="$WP_ROOT" "$WP_ROOT/db_$BACKUP_TIME.sql" --allow-root
# Create a compressed archive of WordPress web root directory
sudo -E tar -jcvf $BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2 -C $WP_ROOT/.. $(basename $WP_ROOT) --ignore-failed-read > /dev/null 2>&1
# Copy backup archive to remote storage using rclone
rclone --config="$RCLONE_CONFIG_FILE" copy "$BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2" wp-backup:wp-files
# List files in remote storage
rclone --config="$RCLONE_CONFIG_FILE" lsl wp-backup:wp-files
# Remove local backup archive
rm -rf "$BACKUP_DIR/wp_$BACKUP_TIME.tar.bz2"
#Remove the database SQL dump file
rm -rf "$WP_ROOT/db_$BACKUP_TIME.sql"
# Delete old files from remote storage (older than the defined maximum age)
# Comment out the next line if you don't want to delete old files
rclone --config="$RCLONE_CONFIG_FILE" delete wp-backup:wp-files --min-age "$MAX_BACKUP_AGE"
# Log the entire process
} | tee -a "$LOG_FILE"0 07:39 xmlrpc.php
Save and close the file.
The script uses the following variables to perform WordPress backup tasks:
BACKUP_TIME: Records the date and time when the backup starts, this creates unique file names for each backup copy.WP_ROOT: Defines your WordPress web root directory.BACKUP_DIR: Specifies local backup files directory.RCLONE_CONFIG_FILE: Points to the Rclone configuration file to use when uploading files to your storage bucket.LOG_FILE: Creates a unique log file for each backup process for reference and troubleshooting.MAX_BACKUP_AGE: Sets the maximum age for files to be deleted from your Dekopon Stack Object Storage. In the configuration 7d deletes all files older than 7 days from your storage bucket.Each time you run the above script:
/var/log/ using the tee utility.To successfully create the WordPress database backup, you must run the above script with sudo privileges since WP-CLI command includes the --allow-root option.
Make the script executable.
$ chmod a+x ~/wp-backups.sh
Run the script to verify that it works correctly.
$ sudo /home/webadmin/wp-backups.sh
Output:
Backup time: 2023-11-22_at_10.30.27
Success: Exported to '/var/www/html/db_2023-11-22_at_10.30.27.sql'.
20 2023-11-22 09:29:57.256559544 testfile.txt
14 2023-11-22 10:29:08.863311480 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.29.08.tar.bz2
19445245 2023-11-22 10:29:50.585685794 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.29.47.tar.bz2
19445190 2023-11-22 10:30:08.322695638 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.30.05.tar.bz2
19445290 2023-11-22 10:30:19.755346688 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.30.16.tar.bz2
19445218 2023-11-22 10:30:30.171939971 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.30.27.tar.bz2
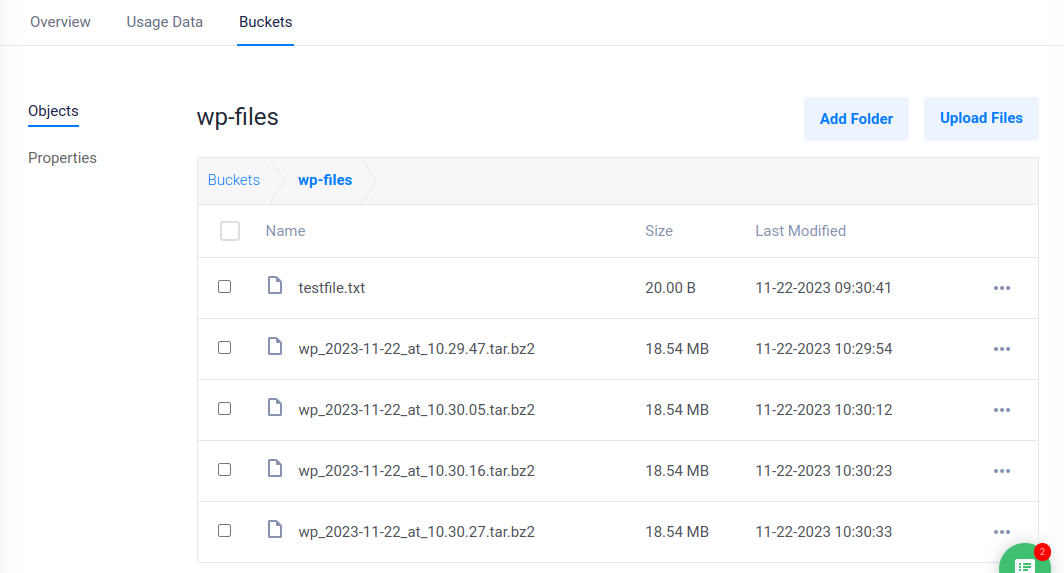
When successful, a new WordPress backup archive is uploaded to your Dekopon Stack Object Storage, and all files in the bucket are listed when the operation is complete.
Access your Dekopon Stack Object Storage dashboard to verify the new WordPress backup files are available in the wp-files bucket.
Edit your Crontab configuration to a new task that automates the WordPress backup script to run once every day.
$ sudo crontab -e
Add the following Cron task to the file.
0 0 * * * /home/webadmin/.wp-backups.shSave and close the file.
The above CronJob executes the wp-backups.sh script once every day and 7 times in a week. This ensures that you have access to daily WordPress backups you can use to restore your site at any time. Depending on your WordPress site activity, adjust the schedule to run daily or weekly. For more information, learn the how to use the Cron task scheduler resource.
To restore your WordPress site from different backup versions stored in your Dekopon Stack Object Storage, use Rclone to pull your target archive file. Depending on your backup files format scheme, you need to extract files from the archive, and transfer them to your new or existing WordPress web root directory to recover your site using the files.
Create a new wp-backups directory to store files downloaded from your Dekopon Stack Object Storage.
$ mkdir -p /home/webadmin/wp-backups
View the available backup archive files stored in your Dekopon Stack Object Storage wp-files bucket.
$ rclone lsl wp-backup:wp-files/
Output:
20 2023-11-22 09:29:57.256559544 testfile.txt
45 2023-11-22 10:29:50.585685794 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.29.47.tar.bz2
90 2023-11-22 10:30:08.322695638 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.30.05.tar.bz2
90 2023-11-22 10:30:19.755346688 wp_2023-11-22_at_10.30.16.tar.bz2
18 2023-11-22 10:30:30.171939971 wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2Note your target backup archive file to restore your WordPress site. For example, wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2.
Copy the backup archive file from Dekopon Stack Object Storage to your new wp-backups directory.
$ rclone copy wp-backup:wp-files/wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2 /home/webadmin/backups/
Switch to your directory.
$ cd ~/backups
List files in the directory and verify that your WordPress backup file is available.
$ ls
Output:
wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2Extract files from the WordPress backup.
$ tar -xvjf wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2
List the directory files and verify the newly extracted WordPress files.
$ ls -l
Output:
example.com
wp_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.tar.bz2In the above output, the new example.com directory is extracted from the backup archive file.
Long list files in the extracted directory and verify that all your WordPress files are available.
$ ls example.com
Output:
total 296
-rw-rw-r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 92719 Nov 22 14:39 db_2023-11-22_at_14.39.09.sql
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 405 Feb 6 2020 index.php
lrwxrwxrwx 1 webadmin webadmin 21 Nov 22 09:17 mysqladmin -> /usr/share/phpmyadmin
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 7211 May 12 2023 wp-activate.php
drwxr-xr-x 9 webadmin webadmin 4096 Nov 9 00:45 wp-admin
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 351 Feb 6 2020 wp-blog-header.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 2323 Jun 14 14:11 wp-comments-post.php
-rw-rw-r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 3516 Nov 22 09:18 wp-config.php
drwxr-xr-x 7 webadmin webadmin 4096 Nov 22 09:18 wp-content
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 5638 May 30 18:48 wp-cron.php
drwxr-xr-x 27 webadmin webadmin 16384 Nov 9 00:45 wp-includes
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 2502 Nov 26 2022 wp-links-opml.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 3927 Jul 16 12:16 wp-load.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 50924 Sep 29 22:01 wp-login.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 8525 Sep 16 06:50 wp-mail.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 26409 Oct 10 14:05 wp-settings.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 34385 Jun 19 18:27 wp-signup.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 4885 Jun 22 14:36 wp-trackback.php
-rw-r--r-- 1 webadmin webadmin 3154 Sep 30 07:39 xmlrpc.phpMove the extracted files to your WordPress web root directory to restore your site.
$ sudo mv example.com /var/www/
Grant the web server ownership permissions to the new web root directory.
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/example.com
Restore your WordPress database using the .sql file in your working directory. Replace example.sql with your actual database backup file.
$ mysql wordpressdb < example.sql
You have implemented an automated backup strategy that creates full WordPress backups using Dekopon Stack Object Storage and Rclone. Depending on your preferences, you must ensure that your WordPress backup files are up to date to roll back changes in case any errors arise from updates or security breaches on your WordPress site.
For more information, visit the following resources: